Nurturing Nobility: A Comprehensive Guide to Vaccinations and Preventive Care for Savannah Cats
Savannah cats, with their striking appearance and wildcat allure, have become sought-after companions for feline enthusiasts. As proud custodians of these majestic creatures, it is our duty to ensure their well-being through a meticulous approach to care. At the heart of responsible ownership lies a robust system of vaccinations and preventive measures. This article serves as a thorough exploration of the essential vaccinations and preventive care required to uphold the health and vitality of Savannah cats, while also shedding light on the optimal frequency of veterinary check-ups.
I. The Crucial Role of Vaccinations:
Vaccinations stand as a front-line defense against a myriad of diseases that could compromise the health of our cherished Savannah cats. Understanding their purpose and the diseases they guard against is fundamental to responsible ownership.
Building Immunity:
- The complex process by which vaccinations bolster the immune system: The intricate process by which vaccinations fortify the immune system in cats is a sophisticated dance of biological responses. When a cat receives a vaccine, it typically contains harmless fragments or weakened forms of the targeted pathogen. In response, the cat’s immune system identifies these foreign elements and initiates a multifaceted defense mechanism. Antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells, engulf the vaccine components and present them to T cells, triggering an immune response.
- T cells, crucial orchestrators in the immune system, activate B cells to produce antibodies specific to the pathogen. Antibodies are proteins that recognize and neutralize the harmful agents, preventing their ability to cause disease. Memory cells, a lasting product of this immune response, ‘remember’ the pathogen’s identity, providing a swift and potent defense upon subsequent exposure. This intricate process not only guards the individual cat against specific diseases but also contributes to the establishment of herd immunity within a feline community.
- In essence, vaccinations empower a cat’s immune system to recognize, remember, and combat potential threats, offering a shield against the complexities of infectious diseases.
- How vaccinations contribute to long-term health and disease prevention: Cat vaccinations play a pivotal role in fostering long-term health and preventing a spectrum of potentially life-threatening diseases. By exposing the immune system to harmless fragments or weakened forms of pathogens, vaccinations prompt the production of antibodies tailored to combat specific diseases. These antibodies, once generated, remain in the cat’s system, creating a defense mechanism that can be rapidly activated upon exposure to the actual pathogen. This process not only shields the individual cat from severe illnesses but also contributes to the broader concept of herd immunity within feline communities. Over the long term, vaccinations substantially reduce the prevalence of infectious diseases, creating healthier environments for both individual cats and the larger cat population.
II. Core Vaccinations for Savannah Cats:
A. Feline Distemper (Panleukopenia):
- The severity and contagious nature of this disease. Feline distemper, also known as panleukopenia, is a highly severe and contagious viral disease affecting cats. The severity lies in its ability to rapidly progress and cause widespread damage to the cat’s immune system, particularly the cells responsible for fighting off infections. This viral infection can lead to a significant drop in white blood cell count, compromising the cat’s ability to fend off other infections. Additionally, feline distemper exhibits a remarkable contagious nature, spreading easily through direct contact with an infected cat or exposure to contaminated environments. Due to its resilience in the environment, feline distemper poses a considerable risk, making timely vaccinations imperative for preventing its devastating effects in cat populations.
- The role of vaccination in preventing Feline Distemper: Vaccination plays a crucial role in preventing Feline Distemper, also known as panleukopenia, by providing a proactive defense against this highly contagious and severe viral disease. The vaccine introduces a harmless form of the virus to the cat’s immune system, prompting the production of antibodies specific to Feline Distemper. These antibodies equip the cat with a robust defense mechanism, effectively neutralizing the virus upon exposure and preventing the development of the severe symptoms associated with the disease.
Feline Calicivirus and Herpesvirus:
- Prevalence and symptoms of upper respiratory infections: Upper respiratory infections (URIs) are common among cats and are often prevalent in crowded or multi-cat environments. Cats with URIs may exhibit symptoms such as sneezing, nasal discharge, coughing, and watery eyes. These infections are typically caused by viruses, such as feline herpesvirus and calicivirus, and can spread easily through close contact, emphasizing the importance of vaccinations to mitigate the prevalence and severity of these respiratory conditions.
- How vaccinations shield against these common feline illnesses: Vaccinations shield against common feline illnesses, such as feline herpesvirus and calicivirus, by training the immune system to recognize and mount a defense against these specific pathogens. The vaccine introduces harmless components of the viruses, prompting the cat’s immune system to produce antibodies that recognize and neutralize the actual viruses upon exposure. This immunological memory, established through vaccinations, ensures a swift and effective response, reducing the severity and duration of the illnesses and, in some cases, preventing infection altogether.
Rabies:
The zoonotic potential of rabies: Rabies, a viral disease affecting mammals, possesses a significant zoonotic potential, meaning it can be transmitted from infected animals to humans. The rabies virus is primarily spread through the saliva of an infected animal, typically through bites. As a potentially fatal disease, understanding and addressing the zoonotic risk of rabies underscores the importance of timely vaccinations for both domesticated and wild animals to prevent its transmission to humans.
- Legal and health implications of keeping vaccinations up to date: Keeping feline vaccinations up to date carries both legal and health implications for cat owners. Many regions have legal requirements mandating certain vaccinations, such as rabies, for domestic cats to prevent the spread of diseases and protect public health. From a health perspective, maintaining up-to-date vaccinations safeguards the individual cat against preventable illnesses, reduces the risk of transmission to other animals, and contributes to the overall well-being of the feline community.
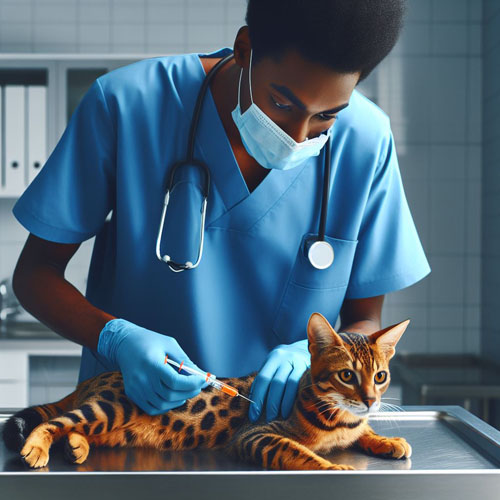
III. Crafting an Appropriate Vaccination Schedule:
Commencing with kittens, the vaccination journey sets the stage for a lifetime of health and vitality. Understanding the timing of vaccinations and the necessity of booster shots is crucial.
Early Vaccination Series:
- The initial vaccinations essential for building a robust foundation: The initial kitten vaccinations are crucial for building a robust foundation of immunity in these young felines. Kittens typically receive a series of vaccinations, including those for feline distemper (panleukopenia), feline calicivirus, and feline herpesvirus, to establish a strong defense against common infectious diseases. Administering these vaccinations at the appropriate stages of kitten-hood lays the groundwork for a healthy and disease-resistant adulthood.
- The significance of precise timing in vaccination schedules: The significance of precise timing in feline vaccination schedules lies in optimizing the effectiveness of the immune response. Kittens receive their initial vaccinations at specific intervals to ensure they are protected during vulnerable stages of development. Adhering to a precise schedule ensures that the immune system is adequately primed to recognize and combat potential pathogens, providing comprehensive protection against infectious diseases throughout the cat’s life.
The Need for Booster Shots:
- How booster shots reinforce and prolong immunity: Feline booster shots play a crucial role in reinforcing and prolonging immunity by reminding the immune system of previously encountered pathogens. These additional doses act as a stimulus to the immune response, prompting the production of more antibodies specific to the targeted diseases. By reinforcing the immune memory, booster shots ensure a heightened and prolonged defense, offering an extended shield against potential infections and contributing to the cat’s long-term health.
- Recommended intervals for booster shots for each core vaccination: The recommended intervals for feline booster shots vary depending on the specific core vaccination. Typically, booster shots for feline distemper (panleukopenia), feline calicivirus, and feline herpesvirus are administered every three years after one year of age, depending on the vaccine type and the cat’s individual health status. Adhering to these recommended intervals ensures that the cat maintains a robust and sustained level of immunity, offering continuous protection against these prevalent and potentially serious feline diseases.
Tailoring Vaccination Plans:
- Recognizing individual factors influencing vaccination needs: Recognizing individual factors influencing feline vaccination needs is crucial for tailoring a personalized and effective immunization plan. Factors such as age, health status, lifestyle, and the cat’s environment all play significant roles in determining the specific vaccines required and the frequency of administration. By taking these individual considerations into account, veterinarians can tailor vaccination schedules to address the unique needs of each cat, optimizing the effectiveness of the immunization process.
- The collaborative role of veterinarians in tailoring vaccination plans: The collaborative role of veterinarians in tailoring vaccination plans is essential for ensuring the optimal health of feline companions. Veterinarians assess individual factors such as the cat’s age, health history, and living conditions to design a customized vaccination schedule. This personalized approach not only addresses the unique needs of each cat but also fosters a strong partnership between pet owners and veterinarians in safeguarding the long-term well-being of feline companions.
IV. Beyond Vaccinations: Holistic Preventive Care:
Comprehensive preventive care extends beyond vaccinations, encompassing regular veterinary check-ups, dental care, parasite control, and nutrition management.
Regular Veterinary Check-ups:
- The importance of routine health assessments: Routine feline health assessments are vital for early detection of potential issues, allowing veterinarians to intervene promptly and maintain optimal well-being. These regular check-ups provide a comprehensive evaluation of a cat’s physical health, dental condition, and overall demeanor. The importance of these assessments lies in their ability to identify and address health concerns before they escalate, contributing to a longer and healthier life for feline companions.
- Frequency variations based on life stages and individual health: The frequency of regular veterinary check-ups for cats varies based on life stages and individual health considerations. Kittens typically require more frequent check-ups, often every three to four weeks, to monitor their growth and administer essential vaccinations. As cats mature, check-up intervals may extend to bi-annual or annual visits, with geriatric cats and those with specific health issues often benefiting from more frequent monitoring to address age-related or individual health concerns.
Dental Care:
- The crucial link between oral health and overall well-being: The crucial link between feline oral health and overall well-being is integral to a cat’s quality of life. Dental issues not only lead to discomfort and pain but can also have systemic effects on a cat’s health, affecting vital organs such as the heart and kidneys. Regular dental care, including professional cleanings and at-home practices, is essential for preventing dental diseases, preserving a cat’s oral health, and contributing to its overall longevity and happiness.
- Practical tips for effective home dental care practices: Effective home feline dental care practices are essential for maintaining optimal oral health. Regular tooth brushing using a feline-specific toothbrush and toothpaste helps prevent plaque and tartar buildup, reducing the risk of periodontal disease. Additionally, providing dental treats, toys designed for dental health, and incorporating specially formulated dental diets into a cat’s nutrition regimen can complement home dental care efforts, ensuring a comprehensive approach to feline oral well-being.:
Nutrition and Weight Management:
- Identification of common parasites affecting Savannah cats: Identification of common parasites affecting Savannah cats is crucial for their overall health and well-being. External parasites such as fleas and ticks can lead to discomfort, skin issues, and transmit diseases, while internal parasites like worms can impact digestive health and nutrient absorption. Regular veterinary check-ups and preventive measures, including appropriate medications, are vital for early detection and effective management of these common parasites in Savannah cats.
- The role of regular flea and tick control in preventive care: Identification of common parasites affecting Savannah cats is crucial for their overall health and well-being. External parasites such as fleas and ticks can lead to discomfort, skin issues, and transmit diseases, while internal parasites like worms can impact digestive health and nutrient absorption. Regular veterinary check-ups and preventive measures, including appropriate medications, are vital for early detection and effective management of these common parasites in Savannah cats.
- The significance of a balanced diet in preventive care: The significance of a balanced diet for Savannah cats cannot be overstated in preventive care. A well-formulated and nutritionally balanced diet is crucial for maintaining overall health, preventing obesity, and minimizing the risk of nutritional deficiencies. Providing a diet that meets the specific dietary needs of Savannah cats, including high-quality protein and essential nutrients, is essential for their long-term well-being and contributes to a proactive approach in preventing diet-related health issues.
- Addressing obesity risks and strategies for weight management: Addressing obesity risks and implementing effective weight management strategies is essential for the well-being of Savannah cats. Obesity in these cats can lead to various health issues, including diabetes, joint problems, and cardiovascular issues. By promoting portion control, engaging in regular play and exercise, and consulting with a veterinarian to establish a tailored diet plan, owners can actively mitigate obesity risks and ensure the long-term health of their Savannah feline companions.
Conclusion:
In the intricate dance of Savannah cat ownership, vaccinations and preventive care emerge as the guardians of health and vitality. Through a diligently crafted vaccination schedule, regular veterinary check-ups, and holistic preventive measures, we honor the nobility of our feline companions. In nurturing the well-being of Savannah cats, we not only preserve their majestic lineage but also pave the way for a legacy of health, happiness, and cherished companionship for generations to come.
Keywords: Savannah Cats, Vaccinations, Preventive Care, Health Guidelines, Responsible Ownership